https://opensource.com/article/21/12/apache-shardingsphere?sc_cid=7016000000127ECAAY
Apache ShardingSphere is an open source distributed database, plus an ecosystem users and developers need for their database to provide a customized and cloud-native experience.
Apache ShardingSphere is an open source distributed database, plus an ecosystem users and developers need for their database to provide a customized and cloud-native experience. In the three years since it joined the Apache Foundation, the ShardingSphere core team has worked hard with the community to create an open source, robust, and distributed database and a supporting ecosystem.
ShardingSphere doesn’t quite fit into the usual industry mold of a simple distributed database middleware solution. ShardingSphere recreates the distributed pluggable system, enabling actual user implementation scenarios to thrive and contributing valuable solutions to the community and the database industry.
The aim of ShardingSphere is the Database Plus concept. More Great Content
- Free online course: RHEL technical overview
- Learn Advanced Linux Commands
- Download Cheat Sheets
- Find an Open Source Alternative
- Read Top Linux Content
- Check out open source resources
Database Plus
Database Plus sets out to build a standard layer and an ecosystem layer above the fragmented database’s basic services. A unified and standardized database usage specification provides for upper-level applications, and the challenges faced by businesses due to underlying databases fragmentation get minimized as much as possible. To link databases and applications, it uses traffic and data rendering and parsing. It provides users with enhanced core features, such as a distributed database, data security, database gateway, and stress testing.
ShardingSphere uses a pluggable kernel architecture for Database Plus. That means there’s modularity, which provides flexibility for the user. There are a few different layers:
- Foundation layer: Provides a variety of access terminals and access forms to meet users’ needs in different scenarios.
- Plugin layer: Provides infrastructure support by enabling extensibility.
- Function layer: Provides a variety of functional plugins that meet users’ needs, allowing users a high degree of flexibility in plugin choice and combination.
- Product layer: This is the layer end users see. This provides them with industry-oriented and specific scenario-oriented products. In other words, it gives the users the right tools for whatever job they’re doing.
database-plus-platform.png
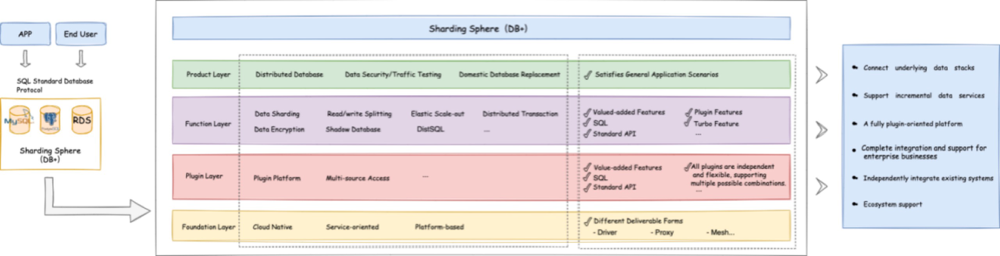
(Trista Pan, CC BY-SA 4.0)
Standardized cluster management with DistSQL
Apache ShardingSphere features the unique SQL dialect of DistSQL (distributed SQL) to connect all elements of the ShardingSphere ecosystem. As the standard interaction language of the ShardingSphere distributed database ecosystem, DistSQL allows users to use one SQL command to create, modify, or delete a distributed database table or encrypt or decrypt it. DistSQL also supports distributed scheduling management.
distsql.png
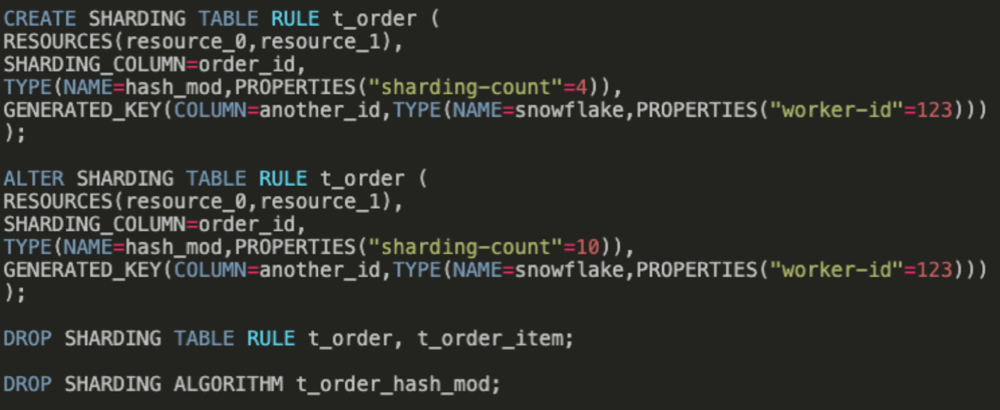
(Trista Pan, CC BY-SA 4.0)
Multi-access terminal
ShardingSphere JDBC and ShardingSphere Proxy have been polished and tested for two years and are now available in production. Many community users provided relevant production community cases.
Thanks to the shared core architecture, and different ShardingSphere adapters, users can choose hybrid adapter deployments if their production environment requires them to do so (shown in the figure below).
hybrid-deployment.png
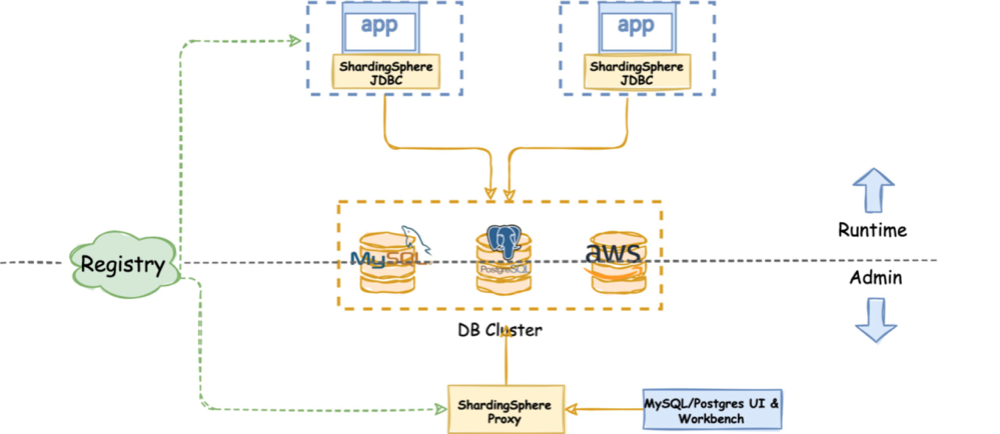
(Trista Pan, CC BY-SA 4.0)
Distributed governance
In the ShardingSphere ecosystem, where computing and storage are separated, there’s the ability for distributed governance of databases so you can maintain many storage nodes, computing nodes, implement circuit breakers, and ensure high availability.
distributed-governance.png
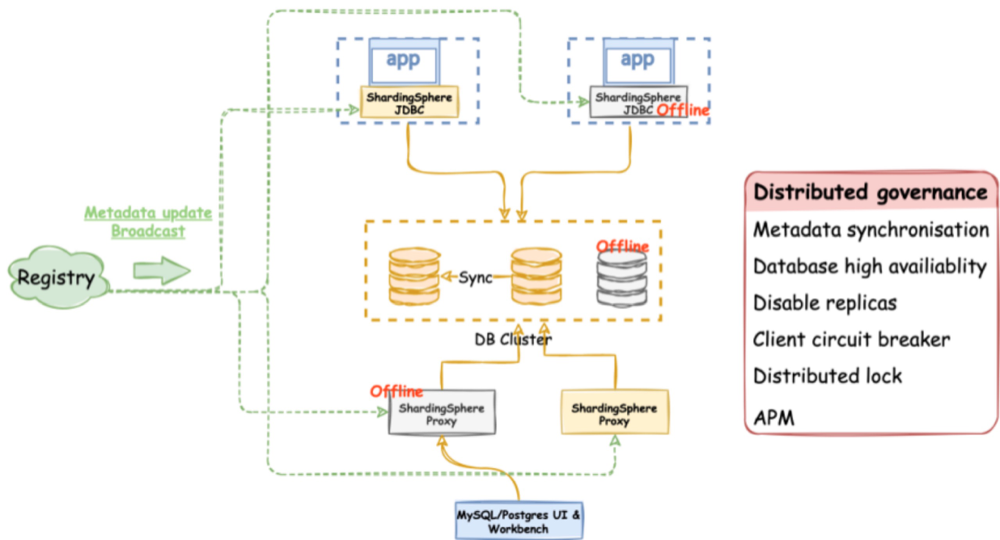
(Trista Pan, CC BY-SA 4.0)
Monitoring with Grafana
ShardingSphere also has status indicators to monitor your infrastructure. The agent dynamic loading mechanism provides you with metrics and tracing indicators, making it convenient to integrate the APM system with a Grafana dashboard.
grafana-dashboard.png
(Trista Pan, CC BY-SA 4.0)
Distributed database for a distributed community
The community is continuing to optimize ShardingSphere and to integrate new ideas and industry scenarios. The community built it, and one of the main driving forces of development is user feedback. That’s a feature of open source, but it’s also a method of practice for this team. The core team members of the ShardingSphere community are happy to mentor anyone interested in open source and provide practice issues for students interested in helping in development. The team also hopes that new friends or contributors will join the community, promote the open exchange of ideas, and create a truly global developer community.

Build a data sharding service with DistSQL
Database sharding demonstrates the additional functionality of DistSQL. Meng Haoran

Monitoring Linux performance with Grafana
Collect stats on your network with a basic install that incorporates collectd, InfluxDB, and Grafana on the same host. Jim Perrin

A guide to database replication with open source
Why choose log-based Change Data Capture (CDC) replication for databases. Learn about the open source options available to you. John Lafleur